IMPEDANCE
Impedance is a measure of how much a circuit resists the flow of electrical current. It is similar to resistance, but it takes into account both the resistance and the reactance of the circuit, which is the measure of how the circuit reacts to changes in the voltage or current.
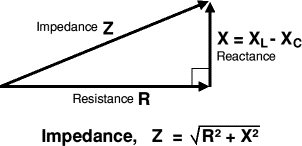
Impedance is represented by the symbol "Z" and is measured in ohms. It is a complex quantity that has both a magnitude and a phase angle. In a simple way, we can think of impedance as the total resistance that a circuit presents to the flow of electrical current, including any effects of capacitance or inductance.
In practical terms, impedance affects how electrical signals are transmitted and received in various types of circuits, such as audio systems, antennas, and power grids. Understanding and controlling impedance is crucial in designing efficient and effective electronic systems.
REACTANCE
Reactance is the measure of how a circuit responds to changes in voltage or current. It is a property of electrical circuits that opposes the flow of electrical current in an AC circuit, unlike resistance which opposes current flow in a DC circuit. Reactance is caused by the presence of inductance or capacitance in the circuit.
Inductive reactance (XL) is the opposition to the change in current flow caused by the presence of inductance in the circuit. It is measured in ohms and is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC signal. As the frequency increases, the inductive reactance also increases.
Capacitive reactance (XC) is the opposition to the change in voltage caused by the presence of capacitance in the circuit. It is also measured in ohms and is inversely proportional to the frequency of the AC signal. As the frequency increases, the capacitive reactance decreases.
Reactance is a crucial parameter in the design and analysis of AC circuits. It affects the behavior of electrical signals and determines the frequency response of the circuit. Reactance, along with resistance, determines the overall impedance of a circuit, which is a measure of its resistance to the flow of electrical current.
RECTIFIER
A rectifier is an electronic device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). The function of a rectifier is to allow current to flow in only one direction, effectively filtering out the negative portion of the AC waveform. This is achieved by using diodes, which are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction.
Rectifiers are commonly used in power supplies to convert AC power from the mains to a DC voltage that can be used to power electronic devices. They are also used in other applications where DC power is required, such as battery charging, electroplating, and welding.
There are two main types of rectifiers: half-wave and full-wave. Half-wave rectifiers use only one diode to convert AC to DC, while full-wave rectifiers use four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration to achieve a more efficient conversion. The output of a rectifier is typically smoothed using capacitors or other filtering components to remove any remaining AC ripple and provide a stable DC voltage.
THYRISTOR
Thyristor is a type of semiconductor device that acts as a switch. It is capable of controlling high voltages and currents in electronic circuits. The function of a thyristor is to allow current to flow freely in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction until a trigger signal is applied. Once triggered, it remains conductive until the current flowing through it drops below a certain threshold. Thyristors are commonly used in applications such as power control, voltage regulation, and motor control.